Kicking off with What is a Crypto Wallet and How to Use It, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone for an informative journey into the world of cryptocurrency wallets.
Exploring the ins and outs of crypto wallets, we delve into their significance, types, setup process, and practical usage to empower you in the digital asset realm.
What is a Crypto Wallet?
Cryptocurrency wallets are digital tools that allow users to store, send, and receive digital assets securely in the world of cryptocurrencies. These wallets are essential for managing various cryptocurrencies and ensuring the safety of your investments.
Types of Crypto Wallets, What is a Crypto Wallet and How to Use It
- Hardware Wallets: These are physical devices that store your cryptocurrency offline, making them highly secure from online hacking attempts. Examples include Ledger Nano S and Trezor.
- Software Wallets: These are digital applications or online platforms that allow users to store their cryptocurrencies. Examples include Coinbase, Exodus, and Trust Wallet.
- Paper Wallets: Paper wallets are physical documents containing your public and private keys, making them an offline way to store your cryptocurrency securely. Users can generate paper wallets using services like Bitaddress.org.
Types of Crypto Wallets
When it comes to storing your precious crypto assets, there are different types of wallets you can choose from. Each type comes with its own set of features, security measures, and convenience levels.
Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices that store your private keys offline, making them highly secure against online hacking attempts. They are considered one of the safest options for storing large amounts of cryptocurrencies.
Software Wallets
Software wallets are applications or programs that can be installed on your computer or mobile device. They are convenient for everyday use and transactions, but they are more susceptible to cyber attacks compared to hardware wallets.
Paper Wallets
Paper wallets involve printing out your private keys and public addresses on a piece of paper. They are completely offline, making them immune to online threats. However, they can be easily damaged, lost, or stolen if not stored properly.
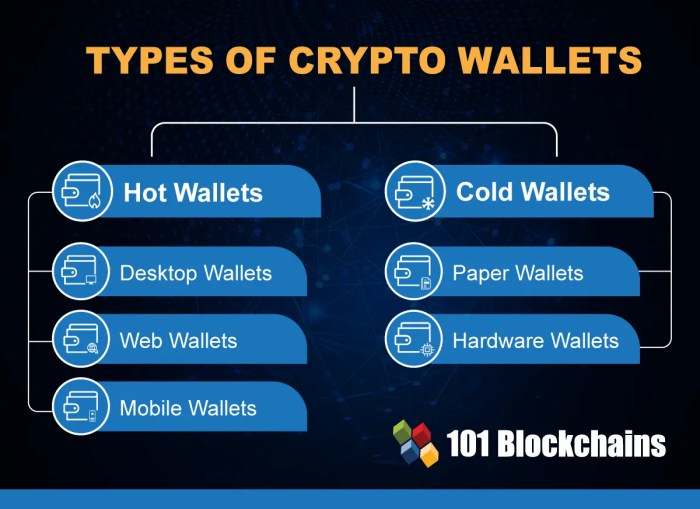
Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets
Hot wallets refer to wallets that are connected to the internet, allowing for quick and easy access to your funds. They are suitable for frequent trading and transactions but are more vulnerable to cyber attacks. On the other hand, cold wallets are offline storage devices, providing extra security as they are not connected to the internet. They are ideal for long-term holding of cryptocurrencies.
How to Set Up a Crypto Wallet?: What Is A Crypto Wallet And How To Use It
Setting up a crypto wallet is essential for anyone looking to store, send, or receive cryptocurrency. Here is a step-by-step guide for beginners on how to create a new wallet, generate a public address, and secure private keys.
Creating a New Wallet
To create a new crypto wallet, you will need to choose a reputable wallet provider. This can be a hardware wallet, a software wallet, or an online wallet. Follow the provider’s instructions to set up your account and create a new wallet.
Generating a Public Address
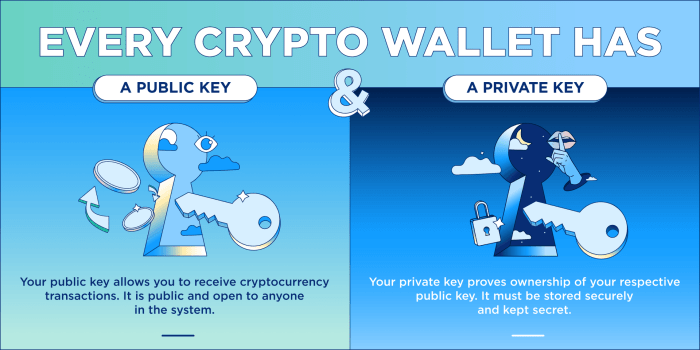
Once your wallet is set up, you will be given a public address. This address is similar to a bank account number and is used to receive cryptocurrency from others. Make sure to share this address with those you want to receive funds from.
Securing Private Keys
Private keys are like passwords that allow you to access your cryptocurrency. It is crucial to keep your private keys secure and never share them with anyone. Consider storing them offline or using a secure password manager to keep them safe.
Choosing a Reputable Wallet Provider
When selecting a wallet provider, make sure to choose one with a good reputation in the crypto community. Look for reviews and recommendations from other users to ensure the safety and security of your funds.
Best Practices for Keeping Your Wallet Secure
– Enable two-factor authentication for an extra layer of security.
– Regularly update your wallet software to protect against vulnerabilities.
– Backup your wallet and private keys in multiple secure locations.
– Be cautious of phishing scams and only enter your information on trusted websites.
Using a Crypto Wallet

Cryptocurrency wallets are essential tools for managing your digital assets. Here’s how you can send and receive cryptocurrency using a crypto wallet, check your wallet balance, initiate transactions, and monitor transaction history.
Checking Wallet Balance and Initiating Transactions
- To check your wallet balance, simply log into your crypto wallet app or platform and navigate to the balance section. Here, you can see the total value of all the cryptocurrencies stored in your wallet.
- When you’re ready to make a transaction, select the option to send cryptocurrency within your wallet interface. Enter the recipient’s wallet address, specify the amount, and confirm the transaction details before finalizing it.
- Always double-check the recipient’s wallet address to ensure the accuracy of the transaction. Once the transaction is complete, you can monitor its progress in the transaction history section of your wallet.
Managing Multiple Cryptocurrencies and Exchanging Assets
- If you hold multiple cryptocurrencies in a single wallet, you can easily switch between them by selecting the desired cryptocurrency from the wallet interface. This allows you to manage and track different assets conveniently within one platform.
- Some crypto wallets also offer built-in exchange features that allow you to swap one cryptocurrency for another directly within the wallet interface. This can be a quick and seamless way to diversify your portfolio or take advantage of market opportunities.
- When exchanging assets within your wallet, pay attention to the exchange rates and fees involved to ensure you’re getting the best value for your transaction. Always review the transaction details before confirming any exchanges.